Climate change is the defining challenge of our time, and the role of technology in addressing or exacerbating this crisis cannot be overstated. Examining the relationship between climate change and technology is crucial as we navigate the complex web of environmental issues. Are they friends, working hand in hand to combat the ecological crisis, or foes, with technology contributing to the very problems it should help resolve?
This blog will unravel the complex relationship between climate change and technology, exploring the causes, effects, and the crucial role technology plays in both exacerbating and mitigating the crisis.
What is Climate Change?
The steam engine, a game-changer in history, reshaped our world by fueling industrialization and economic growth. However, its heavy use of coal affected the environment during the Industrial Revolution. With no controls, factories freely released pollutants, contributing to climate change. Even today, cities like London bear the environmental scars from the emissions of the 1800s (Power et al., 2018).

At its core, what is climate change? It is not just about a shift in the weather; it is a symphony of disruptions to our planet's delicate balance. Human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, escalate the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, trapping heat and altering our climate.
Causes of Climate Change
Climate change is a complex phenomenon driven by various human activities. Let us break down the key causes of climate change:
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Burning of Fossil Fuels: Coal, oil, and natural gas combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. Massive coal-fired power plants, like those in China and the US, contribute substantial carbon dioxide emissions. China is the world's largest coal consumer, generating approximately 57.7% of its electricity from coal.
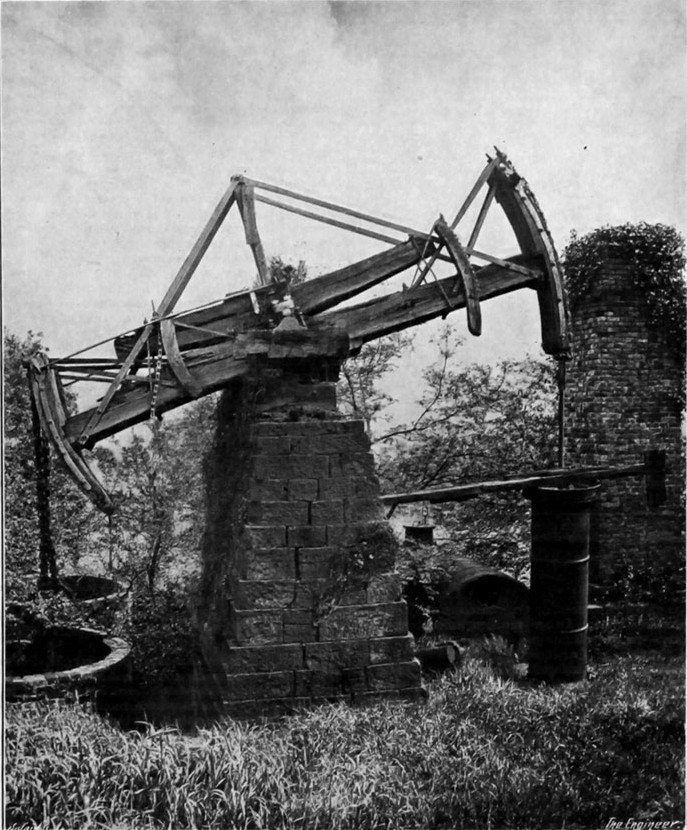
- Deforestation: Clearing forests reduces the number of trees that absorb CO2. In Brazil, the Amazon Rainforest, often called the 'lungs of the Earth,' lost an estimated 10,000 square kilometers in 2019, primarily due to agricultural expansion and logging.

Agricultural Practices
- Livestock Farming: Ruminant animals produce methane during digestion. Brazil, a major beef exporter, has the world's largest commercial cattle herd, contributing to methane emissions.
- Use of Nitrogen-Based Fertilizers: Contributes to nitrous oxide emissions. The United States, a prominent user of nitrogen-based fertilizers, accounted for 15% of global nitrogen fertilizer consumption in 2020.
Land Use Changes
- Urbanization: Conversion of natural landscapes into urban areas contributes to heat absorption and altered climate patterns. Mumbai, India, experienced an urban heat island effect with temperatures up to 5°C higher in densely built areas than surrounding rural regions.

Waste Management
- Landfills: The decomposition of organic waste in landfills produces methane.
- Waste Incineration: Waste incineration in urban areas, such as in countries like Sweden, releases CO2 into the atmosphere, affecting local and global climates. Sweden incinerates about 49% of its municipal waste for energy.
Transportation Emissions
- Combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles: High transportation-related emissions are evident in densely populated cities like Tokyo, where extensive vehicle use contributes to air pollution and climate change. Tokyo, Japan, has over 4.8 million registered vehicles, contributing to elevated carbon emissions and air pollution.

The Role of Technology in Climate Change
As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change, technology emerges as a powerful ally in the fight against environmental degradation. From innovative climate change solutions to sustainable practices, technology plays a pivotal role in mitigating the causes and effects of climate change.
However, technology, often hailed as the hero in our battle against climate change, is not without its complications. While solar panels and wind turbines promise a cleaner future, their production and disposal pose environmental challenges. Are these technologies genuine allies in the fight against climate change, or do their drawbacks make them foes in disguise?
Let us take a closer look at how technology impacts climate change, both positively and negatively.
Renewable Energy Technologies
Renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, are transformative in reducing dependence on fossil fuels, decreasing carbon emissions, and fostering a sustainable energy future. The global solar energy capacity reached 713 GW in 2020, a substantial increase from previous years. Furthermore, wind power provided 8% of the world's electricity demand in 2020, a figure expected to rise with ongoing technological advancements.
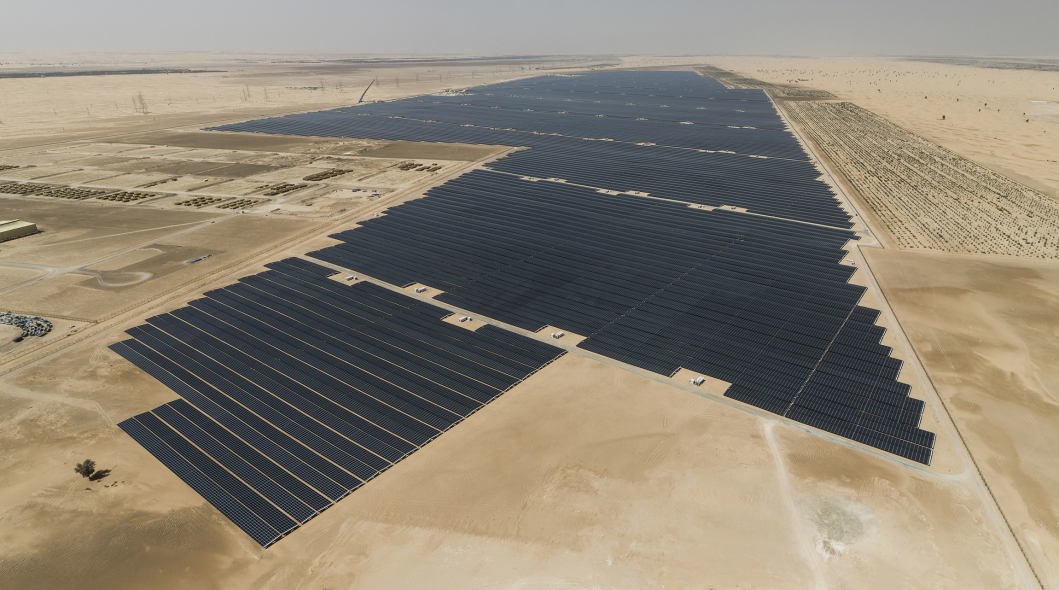

However, producing and disposing of solar panels and wind turbines present environmental challenges. The manufacturing process involves using rare earth elements and potentially hazardous materials, contributing to ecological impacts. Additionally, disposing of outdated or damaged components poses challenges in recycling and waste management, potentially releasing harmful substances into the environment.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Technologies
Using carbon capture and storage technology to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industries and power plants prevents the release of CO2 into the atmosphere. As of 2020, 26 commercial CCS facilities operated globally, capturing approximately 40 million metric tons of CO2 annually.
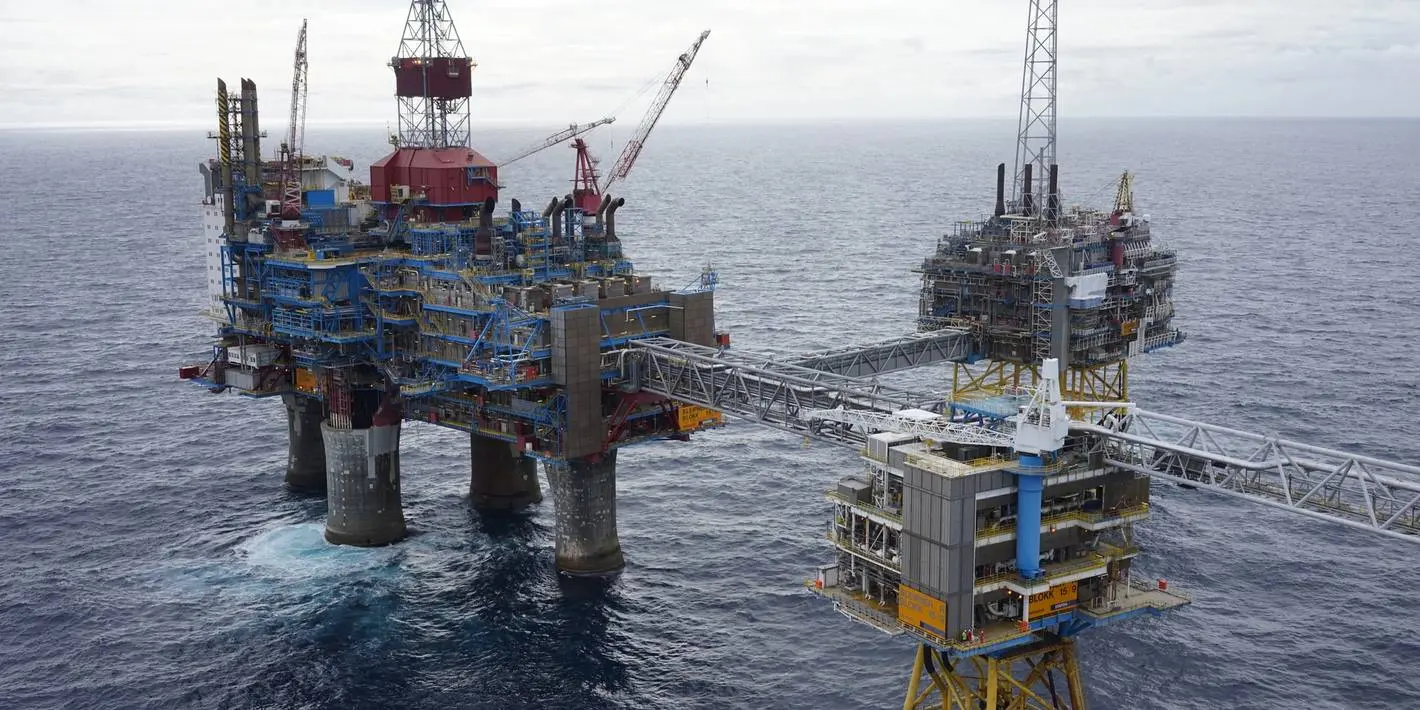

Unfortunately, the energy-intensive capture processes, high implementation costs, and the limited availability of suitable storage sites pose challenges. Furthermore, the risk of potential leakage and the concern that heavy reliance on CCS might defer the transition to renewable energy sources add complexity to their effectiveness.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Sustainable Transportation
Adopting electric vehicles and sustainable transportation technologies reduces reliance on fossil fuels, curbing emissions from the transportation sector and promoting eco-friendly mobility solutions. The global electric vehicle market is projected to reach $985.72 billion by 2027, reflecting a shift toward sustainable transportation and mitigating the effects of climate change.
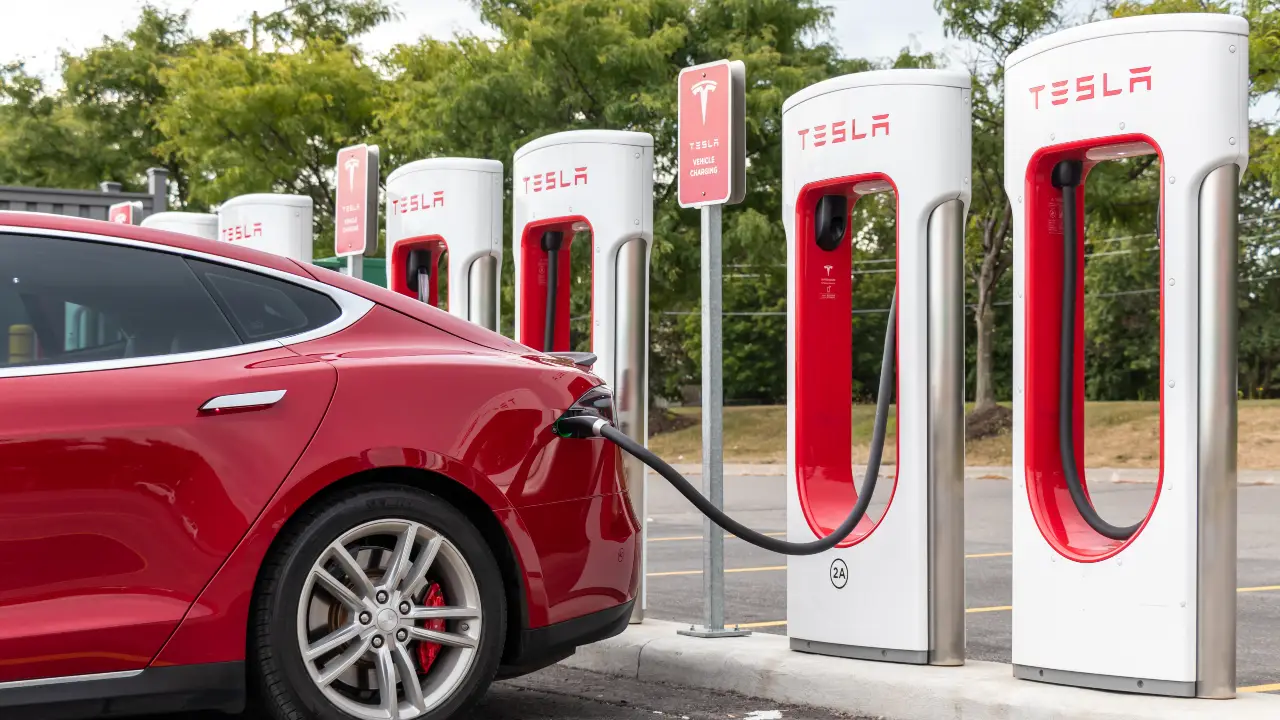

Despite their positive contributions to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, electric vehicles are not without environmental concerns. The production and disposal of EV batteries involves extracting raw materials with associated environmental and social impacts. Additionally, the environmental effectiveness of EVs is contingent on the energy sources used for charging, and reliance on non-renewable energy can compromise their overall carbon footprint.
Blockchain Technology for Carbon Credits
Blockchain technology ensures transparency and accountability in carbon credit markets, fostering trust and incentivizing businesses to engage in sustainable practices. The blockchain market for carbon offset projects is expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2026, providing transparency and efficiency in carbon credit transactions.

While Blockchain technology for carbon credits is hailed as a promising solution for enhancing transparency and efficiency in carbon markets, there are potential negative effects. The energy-intensive process of validating and recording transactions on blockchain networks, particularly in proof-of-work systems, can contribute to carbon emissions. Additionally, the rapid growth of blockchain technologies may lead to increased electronic waste from outdated hardware.
Smart Cities and Sustainable Infrastructure
Developing smart cities and sustainable infrastructure, exemplified by projects like Singapore's Smart Nation Initiative, uses technology to optimize resource use, enhance energy efficiency, and improve urban living. The initiative incorporates advanced sensor networks and data analytics to monitor and manage energy consumption, waste management, and transportation systems.

However, the production and deployment of these technologies contribute to electronic waste, with global e-waste estimated at 53.6 million metric tons in 2019.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Climate Modeling and Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence's role in climate research is exemplified by projects like Google's DeepMind, using AI to improve predictions of wind power generation, enhancing the efficiency of renewable energy sources.
However, the energy consumption associated with training sophisticated AI models is substantial, with a single deep-learning model emitting as much carbon as five cars over their lifetime. Balancing the benefits of AI-driven climate insights with the environmental costs of computational power remains a challenge.
Biotechnology for Climate-Resilient Agriculture
Developing drought-tolerant crops like genetically modified maize illustrates biotechnology's impact on climate-resilient agriculture. Projects such as the Water Efficient Maize for Africa (WEMA) initiative have introduced genetically modified maize varieties to increase yields in regions susceptible to drought.

However, debates persist regarding genetically modified organisms' safety and ecological impact. The global cultivation of genetically modified crops reached 191.7 million hectares in 2018, with concerns about biodiversity loss and long-term environmental consequences (ISAAA, 2018).
Final Verdict: Friends or Foes?
In wrapping up our exploration, think of the relationship between climate change and technology as a gripping storyline. So, are climate change and technology friends or foes? The answer lies in our hands. Technology, when wielded responsibly, becomes a powerful ally. It offers solutions to mitigate the damage we have inflicted on our planet.
As stewards of this planet, we must harness the potential of technology to usher in an era where our actions contribute to healing rather than harming. However, blind reliance on technology without addressing the root causes of climate change or changing our consumption patterns can turn it into a foe. The key lies in balance – a delicate equilibrium where technology complements our efforts to create a sustainable future.
The Tech Junction is the ultimate hub for all things technology. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or simply curious about the ever-evolving world of technology, this is your go-to portal. If you want to write for us or have any feedback feel free to email us.